How to Become an Ultrasonographer: Essential Education and Certifications
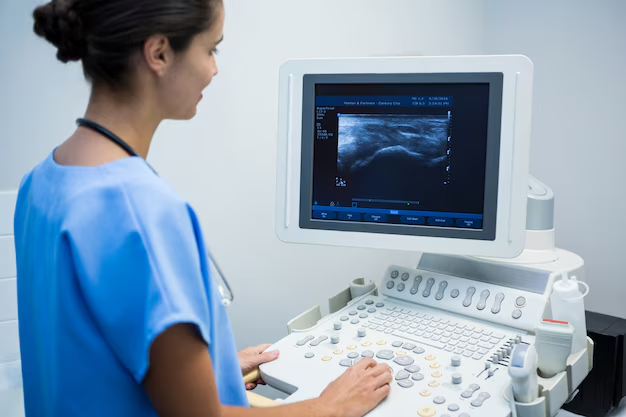
Becoming an ultrasonographer is a fulfilling career choice for those interested in the medical field, especially for individuals drawn to diagnostic imaging and patient care. To embark on this rewarding path, prospective ultrasonographers typically begin by pursuing a dedicated educational route. A minimum of an associate degree in diagnostic medical sonography is essential, although a bachelor's degree might be preferred by some employers. Besides formal education, programs accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) are highly recommended, as they provide a robust foundation in both theoretical and practical aspects.
Once you have earned your degree, obtaining certification is a pivotal step in establishing credibility and enhancing employment prospects. Most employers seek candidates who hold certifications from recognized bodies such as the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). This certification signifies an individual's competence in the field and often requires passing a rigorous exam. In some states, obtaining a specific license may also be necessary to practice legally. By investing in a comprehensive educational experience and obtaining the right certifications, aspiring ultrasonographers can set themselves up for a successful and impactful career in healthcare.
Pathway to Becoming an Ultrasonographer:
- 🎓 Associate Degree in Diagnostic Medical Sonography
- 🎓 Bachelor's Degree in Medical Sonography (optional but beneficial)
- 🔍 CAAHEP-Accredited Program Completion
- 📜 ARDMS Certification
- 🏅 State License (where applicable)