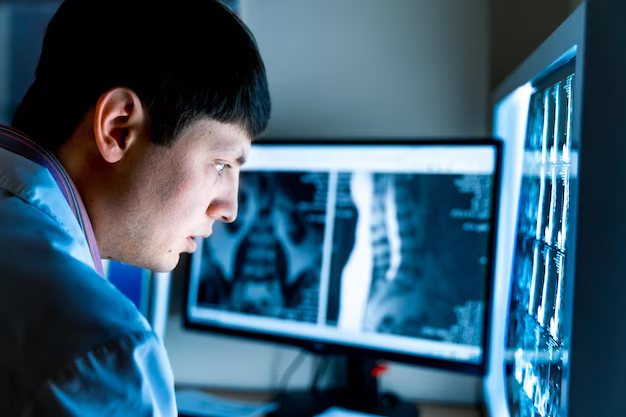
How to Become a Diagnostic Radiologist: Required Education and Certifications
Embarking on a career as a diagnostic radiologist involves a structured educational path that prioritizes an in-depth understanding of medical imaging and patient care. Aspiring radiologists begin their journey with a bachelor's degree in a science-related field, providing a strong foundation in critical thinking and technical skills. Following this, candidates must attend medical school, earning either an MD or DO degree, where they learn the relationship between diagnostic imaging and overall healthcare.
Upon completing medical school, the next step involves specialized training in a residency program focused on diagnostic radiology, typically lasting four to five years. It's in these programs that aspiring radiologists hone their expertise in interpreting medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. After residency, obtaining board certification from the American Board of Radiology (ABR) is strongly recommended. This prestigious certification not only validates proficiency in the field but also enhances career opportunities. Continual education and staying abreast of advances in imaging technology are crucial for success in this fast-evolving medical specialty.
Educational Path and Certifications to Become a Diagnostic Radiologist:
- 🎓 Bachelor's Degree: Preferably in a science-related field
- 🩺 Medical Degree (MD or DO): Completion of medical school
- 🏥 Residency in Diagnostic Radiology: 4-5 years of specialized training
- 📜 Board Certification: American Board of Radiology (ABR) Certification (highly recommended)
- 🔄 Continuing Education: Ongoing learning and specialization in new technologies and techniques