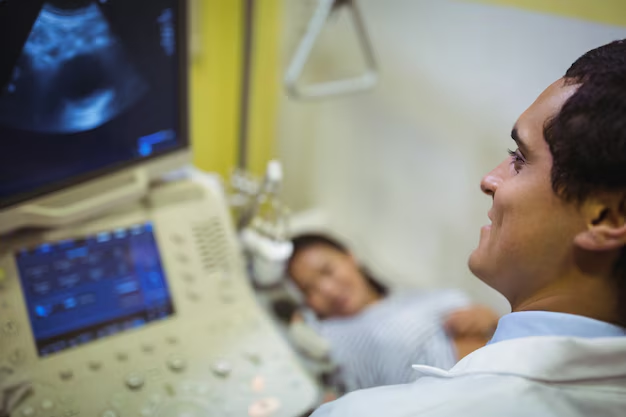
How to Become a Cardiac Sonographer: Essential Degrees, Certifications, and Licenses
Embarking on a career as a cardiac sonographer offers a unique blend of healthcare technology and patient interaction, requiring specialized education and certification. To truly excel in this field, candidates typically pursue an Associate degree in Diagnostic Medical Sonography, which provides fundamental knowledge in anatomy, physiology, and imaging technology. Some opt for a Bachelor's degree, broadening their expertise and opening doors to advanced career opportunities. While degrees provide foundational knowledge, certification is often mandatory. The American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) offers credentials such as the Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer (RDCS) certification, vital for showcasing your professionalism and competence to future employers.
Beyond degrees and certifications, practical experience through accredited programs ensures a deep understanding of echocardiograms and patient care practices. Licensure, though not universally required across all states, can further enhance your qualifications. Engaging in continuing education keeps you at the forefront of advances in cardiac sonography, fostering both personal and professional growth. Exploring educational pathways can be a prudent step towards this rewarding profession, aligning with institutions dedicated to excellence in healthcare education.
Key Educational Pathways and Credentials to Explore:
- 🎓 Associate Degree in Diagnostic Medical Sonography
- 🎓 Bachelor’s Degree in Sonography or Related Health Science
- 📜 Certified Sonographer through the ARDMS
- 📋 Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer (RDCS) Certification
- 📘 Continuing Education Programs and Workshops